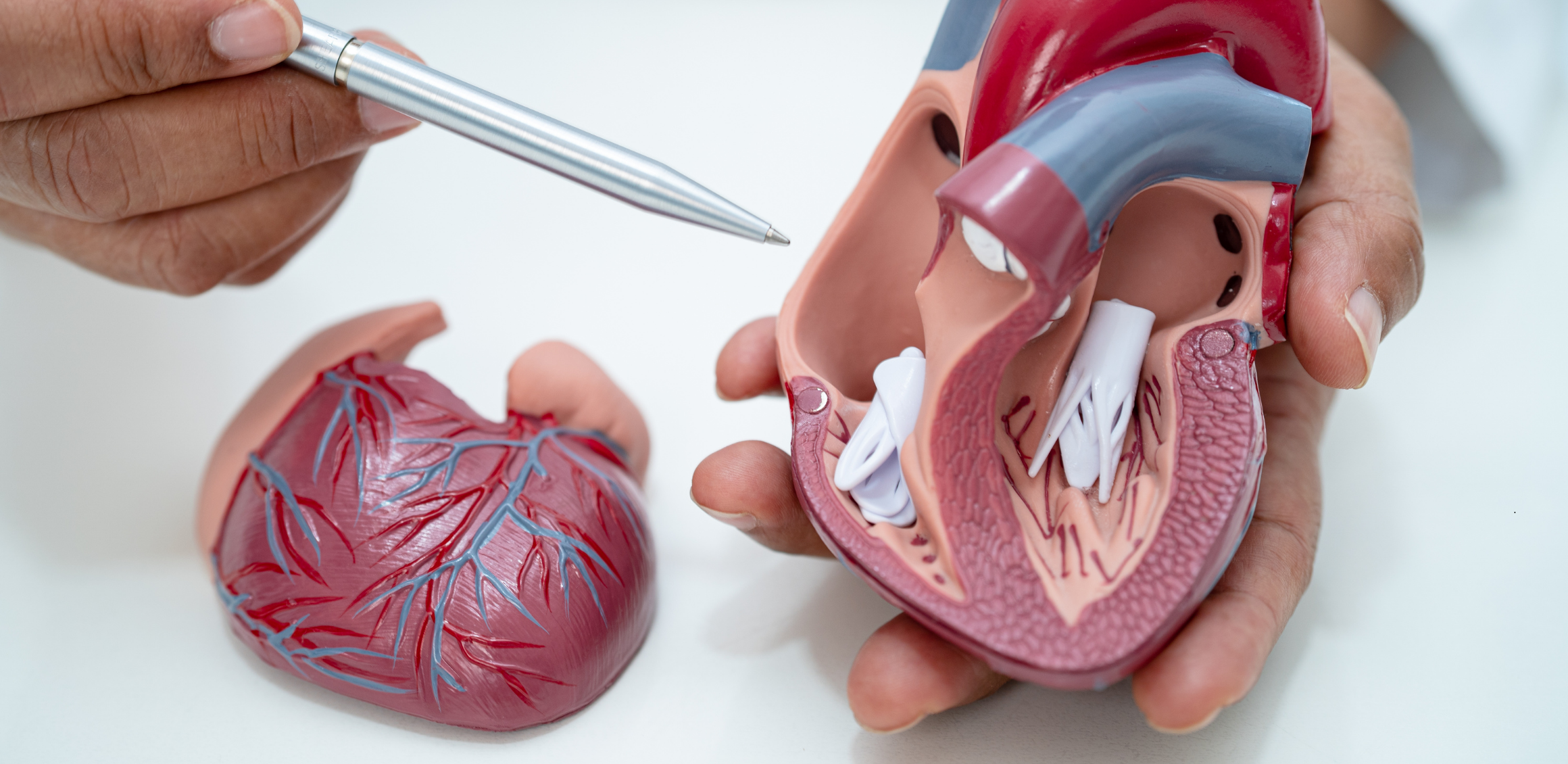
Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) encompass a wide array of medical conditions affecting the heart (cardiac) and blood vessels (vascular).
Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) encompass a wide array of medical conditions affecting the heart (cardiac) and blood vessels (vascular). These conditions collectively impact the functionality and health of the cardiovascular system.
Definition of Cardiovascular Diseases: Cardiovascular diseases refer to a spectrum of health issues that impair the functions of the heart and blood vessels. This category includes conditions such as heart attacks, strokes, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), heart failure, arterial blockages (atherosclerosis), hypertension (high blood pressure), peripheral artery diseases (including vascular conditions affecting the legs), and various other disorders.
Causes of Cardiovascular Diseases: Several factors contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases. These include hypertension, hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol levels), obesity, diabetes mellitus, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, stress, genetic predisposition, and specific lifestyle habits. Furthermore, certain medical conditions (e.g., rheumatic diseases) can also increase susceptibility to cardiovascular diseases.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Diseases: Symptoms associated with cardiovascular diseases can vary significantly depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms include chest pain or discomfort, dyspnea (shortness of breath), palpitations, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, lower extremity edema (swelling in the legs), and peripheral cyanosis (coldness or numbness in the extremities). However, some cardiovascular diseases may progress asymptomatically, emphasizing the importance of regular medical check-ups for early detection.
Treatment and Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases: Treatment strategies for cardiovascular diseases are tailored based on the type, severity, and overall health status of the patient. Treatment modalities may involve pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications (such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation), invasive procedures (like stent implantation, cardiac surgeries), rehabilitation programs, and supportive therapies.
Preventive measures against cardiovascular diseases focus on adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining regular physical activity, adhering to a balanced diet, limiting tobacco and alcohol consumption, managing stress effectively, undergoing periodic health screenings, and achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight. Regular communication with healthcare providers is crucial, particularly for individuals with familial predispositions or specific health conditions.
Conclusion: Cardiovascular diseases pose significant health risks and can lead to life-threatening complications. However, early diagnosis, appropriate treatment interventions, and the adoption of healthy lifestyle practices can substantially mitigate these risks. Therefore, prioritizing routine medical evaluations and embracing healthy lifestyle choices are essential steps toward safeguarding cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
