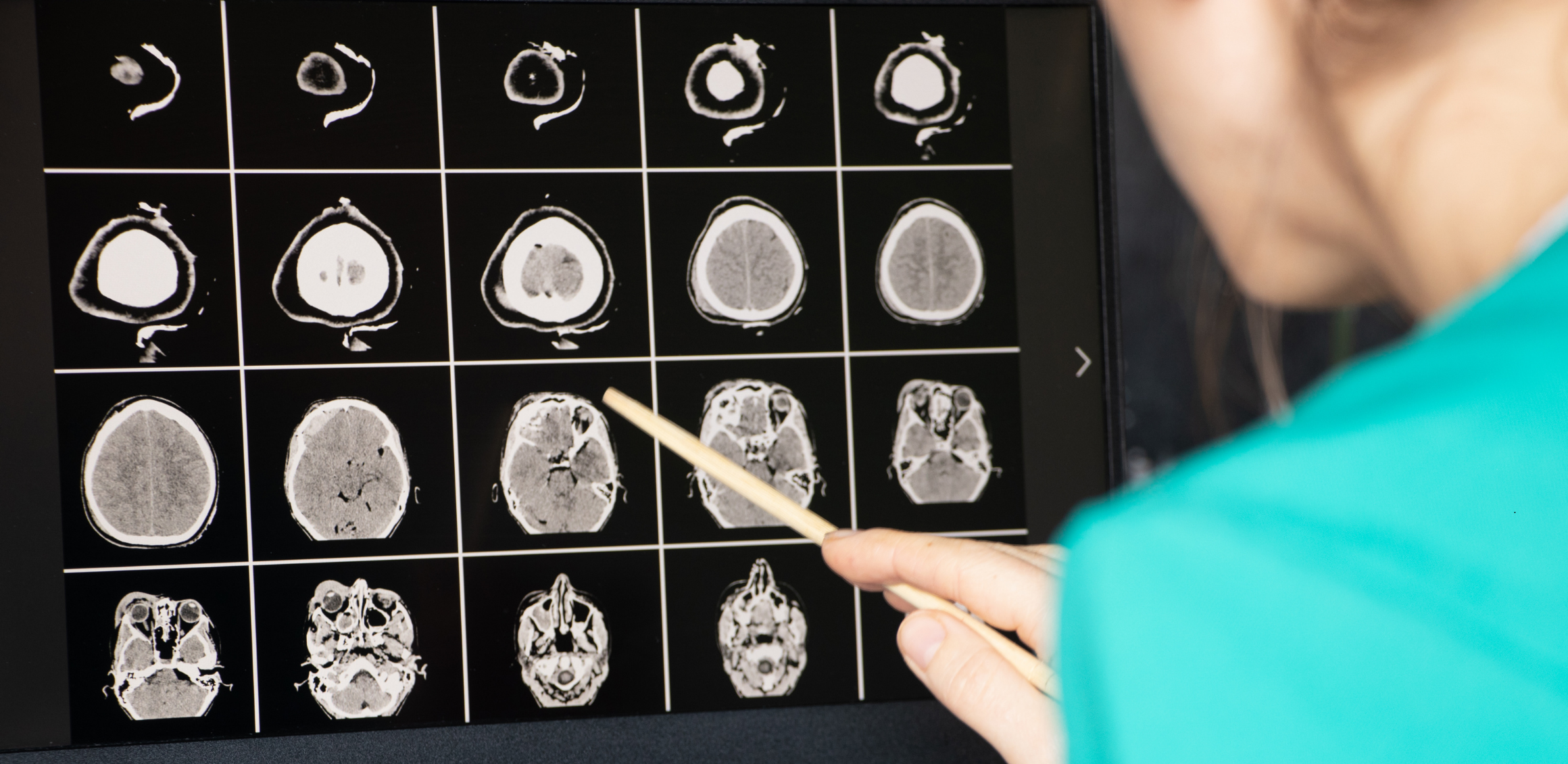
Brain Vascular Diseases
Brain vascular diseases refer to abnormalities or conditions affecting the blood vessels within the brain, which can impact cerebral circulation and lead to serious consequences.
Brain Vascular Diseases
Brain vascular diseases refer to abnormalities or conditions affecting the blood vessels within the brain, which can impact cerebral circulation and lead to serious consequences. Here are some types of brain vascular diseases:
Stroke
Stroke occurs when there is a sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain or when brain blood vessels burst, resulting in damage to brain tissue. Stroke is a serious condition that requires urgent medical intervention. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke (caused by a blockage of blood flow) and hemorrhagic stroke (caused by brain bleeding).
Stroke Symptoms
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision loss or double vision
- Sudden severe headache
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or falling
Brain Aneurysm
A brain aneurysm is a weak spot or balloon-like swelling in the blood vessels of the brain. These aneurysms can rupture, leading to brain hemorrhage, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
Brain Aneurysm Symptoms
- Sudden and severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Vision disturbances
- Difficulty speaking
- Neurological symptoms such as weakness or numbness
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain that is present from birth. It involves abnormal connections between arteries and veins, causing blood to flow differently than normal. The rupture or bleeding of an AVM can cause severe damage to brain tissue.
AVM Symptoms
- Headache
- Seizures
- Stroke-like symptoms
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neurological symptoms such as weakness or numbness
Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of brain vascular diseases depend on the type and severity of the condition. In cases of stroke, immediate medical intervention may be necessary, while conditions like brain aneurysms or AVMs may require surgical intervention or interventional procedures such as embolization. Preventive measures include adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and maintaining controlled blood pressure. Patients and their families should be educated about recognizing symptoms, reducing risk factors, and preparing for emergencies.
