- TAVI
- Tri-Klip
- Complex Coronary Interventions
- CTO Treatment (Chronic Total Occlusion)
- Balon Mitral Valvuloplasti
- Pulmonary Balloon Valvuloplasty
- Septal Ablation
- ASD (Atrial Septal Defect)
- Coronary Arteriovenous Fistula Closure
- Paravalvular Leak Closure
- Ablation Methods for Tachycardias
- Supraventricular Tachycardias
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Epikardial Ablation
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery
- Lead Extraction
- Device Implantations
- Pacemaker / ICD
- CRT / CRT-D Implantation
- Wireless Pacemakers
- Renal Denervation
- Non-Surgical Treatment of Aortic Aneurysms and Ballooning
- Cardioneural Modulation
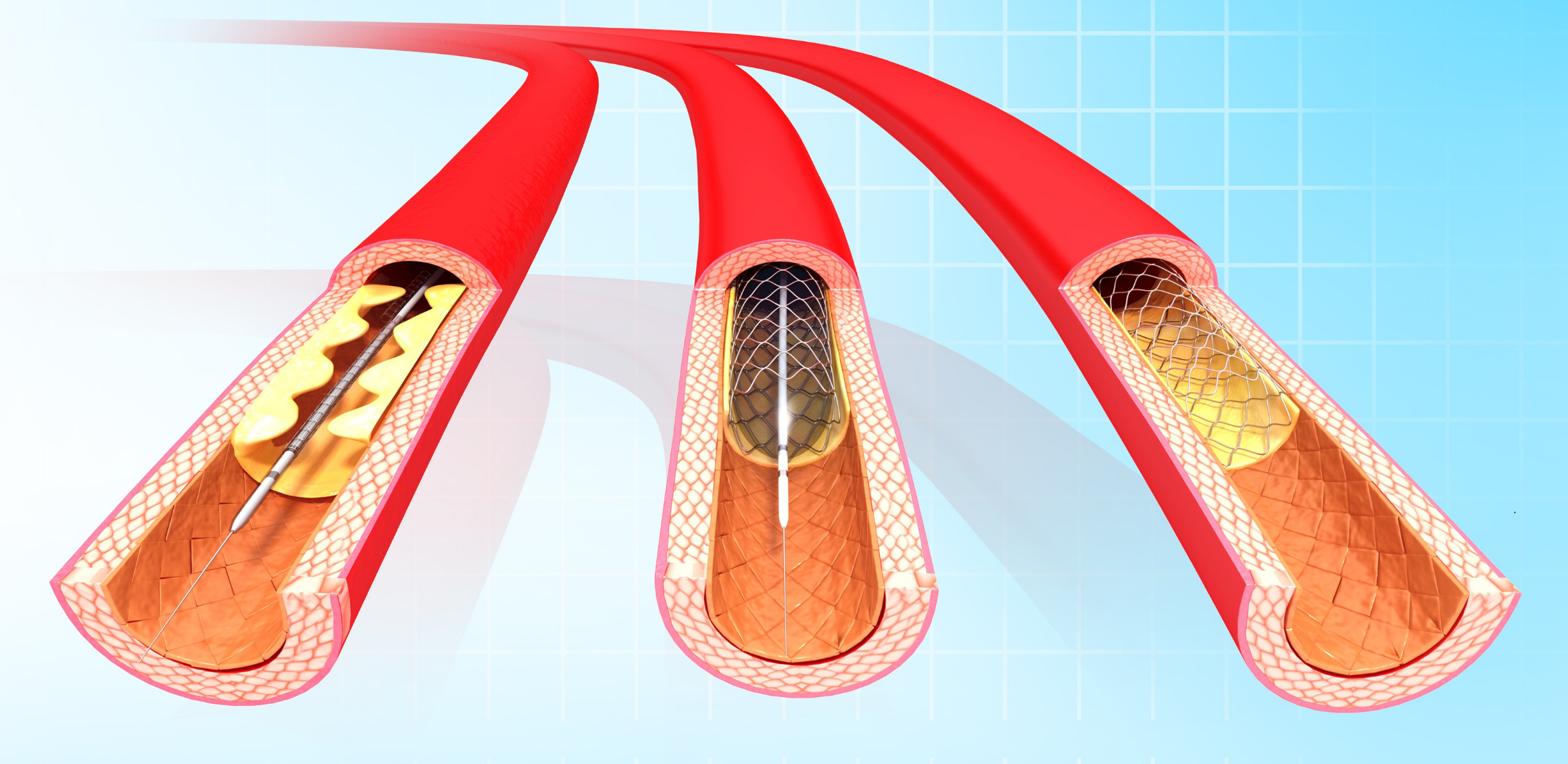
Complex Coronary Interventions
Complex coronary interventions are advanced, minimally invasive procedures used in the treatment of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
Complex Coronary Interventions
Complex coronary interventions are advanced, minimally invasive procedures used in the treatment of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). These interventions are particularly applied in the treatment of complex and high-risk lesions (blockages), which are more challenging than standard balloon angioplasty or stent placement procedures, and are critically important in treating severe conditions such as heart attacks or angina (chest pain).
Types of Complex Coronary Interventions
- Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) Interventions:
- Definition: CTO refers to a condition where a coronary artery is completely blocked, usually for more than 3 months.
- Treatment: Involves using special catheters and wires to open the blockage. This procedure requires high technical expertise and experience.
- Bifurcation Lesions:
- Definition: Bifurcation lesions occur at the point where a coronary artery branches.
- Treatment: It involves opening both branches and placing stents. This procedure is typically performed using two-stent techniques (e.g., Crush or Culotte techniques).
- Left Main Coronary Artery (LMCA) Disease:
- Definition: LMCA is one of the main arteries of the heart affected by disease.
- Treatment: Managed using specialized stents and techniques due to its potential to affect a large area of the heart muscle.
- Calcified Lesions:
- Definition: Calcified lesions are blockages with significant calcium buildup in the artery wall.
- Treatment: Involves the use of atherectomy devices (e.g., rotational or orbital atherectomy) to remove the calcium.
Benefits of Complex Coronary Interventions
- Minimally Invasive: They are less invasive compared to open-heart surgery, leading to faster recovery for patients.
- High Success Rate: When performed by experienced cardiologists, these interventions have a high success rate.
- Improved Quality of Life: They reduce chest pain (angina) and enhance heart function.
- Quick Recovery: Patients can typically resume normal activities within a few days after the procedure.
Risks of Complex Coronary Interventions
- Bleeding: Risk of bleeding at the catheter insertion site.
- Infection: Risk of infection following the procedure.
- Stent Thrombosis: Risk of blood clot formation inside the stent.
- Heart Attack: Risk of heart attack during or after the procedure.
- Arrhythmia: Possibility of developing heart rhythm disturbances.
Post-Procedural Follow-up and Care
After the procedure, patients should attend regular doctor visits and adhere to medications (e.g., blood thinners) as prescribed. Lifestyle changes (such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and smoking cessation) and participation in cardiac rehabilitation programs can help maintain heart health.
Complex coronary interventions play a vital role in treating patients with severe coronary artery disease. When performed by experienced and skilled cardiologists, these procedures significantly improve patients’ quality of life and effectively treat life-threatening conditions.
