- TAVI
- Tri-Klip
- Complex Coronary Interventions
- CTO Treatment (Chronic Total Occlusion)
- Balon Mitral Valvuloplasti
- Pulmonary Balloon Valvuloplasty
- Septal Ablation
- ASD (Atrial Septal Defect)
- Coronary Arteriovenous Fistula Closure
- Paravalvular Leak Closure
- Ablation Methods for Tachycardias
- Supraventricular Tachycardias
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Epikardial Ablation
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery
- Lead Extraction
- Device Implantations
- Pacemaker / ICD
- CRT / CRT-D Implantation
- Wireless Pacemakers
- Renal Denervation
- Non-Surgical Treatment of Aortic Aneurysms and Ballooning
- Cardioneural Modulation
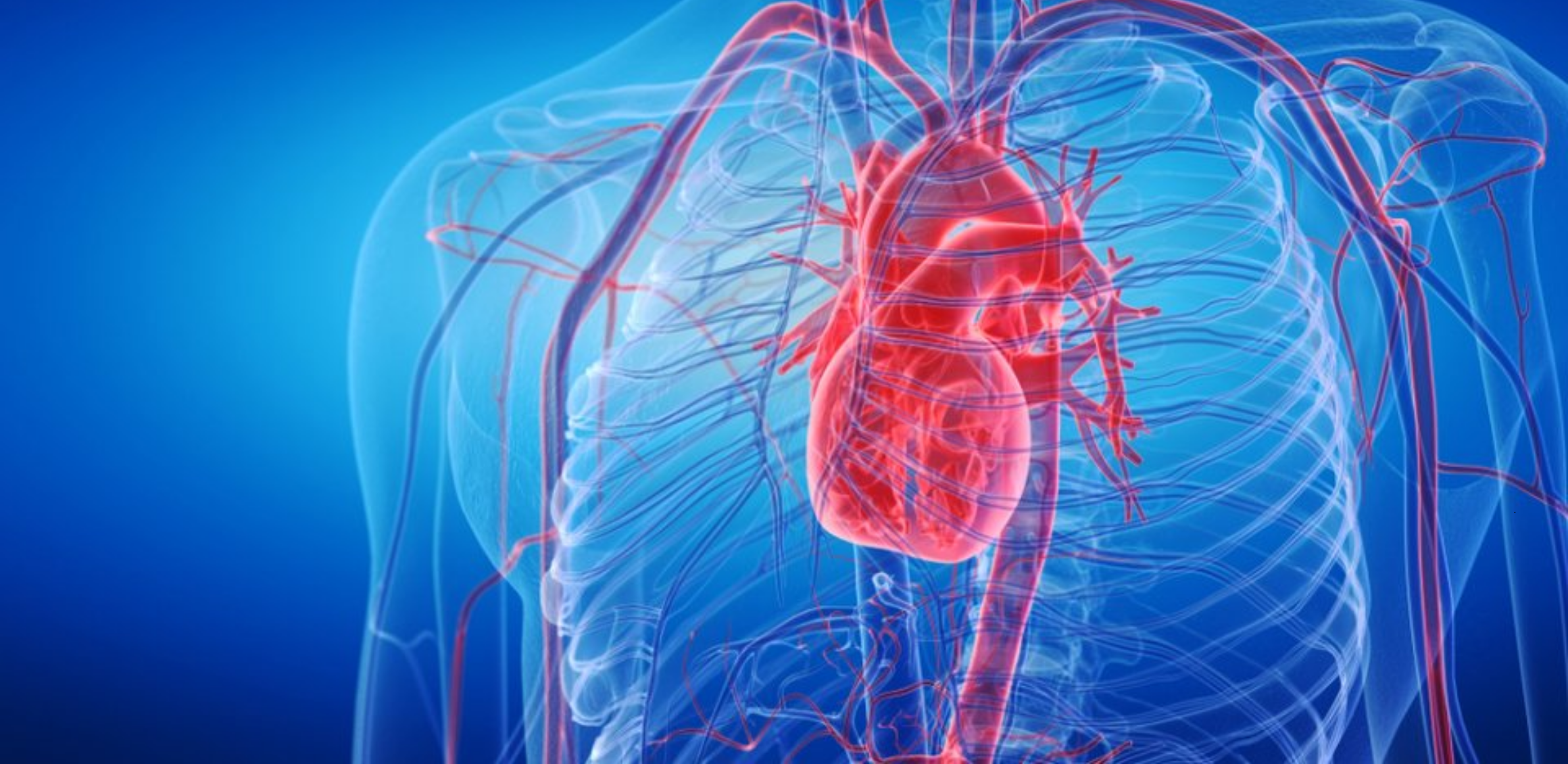
Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) Treatment
Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) treatment is an advanced cardiac procedure used to open long-standing complete blockages in coronary arteries.
Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) Treatment
Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) treatment is an advanced cardiac procedure used to open long-standing complete blockages in coronary arteries. CTOs are among the most challenging and complex forms of coronary artery disease, typically defined as total occlusions lasting more than 3 months. CTO treatment is crucial, especially for patients experiencing severe chest pain (angina) or reduced heart function.
Objectives of CTO Treatment
Restoration of Blood Flow: To restore blood flow in occluded coronary arteries.
Reduction of Chest Pain: To alleviate angina symptoms.
Improvement of Heart Function: To enhance myocardial perfusion and function.
Enhancement of Quality of Life: To enable patients to perform daily activities more comfortably.
Methods Used in CTO Treatment
The primary method for CTO treatment is percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), utilizing catheter-based techniques to open the blockage.
- Retrograde Approach:
- A technique used in CTO treatment where the catheter and wires access the blockage through an artery on the opposite side.
- It is employed particularly when antegrade approaches have failed.
- Antegrade Approach:
- This is the most common technique used in CTO treatment.
- Direct intervention towards the blockage using catheters and wires.
- The occlusion is opened using specially designed guide wires and balloons.
- Dissection-Reentry Techniques:
- Involves crossing the blockage by passing through the arterial wall around it and re-entering the artery.
- Conducted using specialized devices and techniques.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques:
- Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) are advanced imaging techniques used to enhance the success of CTO treatment.
- These techniques provide better visualization of the blockage structure and catheter position.
Advantages of CTO Treatment
- Minimally Invasive: Less invasive compared to open-heart surgery, leading to shorter recovery times.
- Symptom Relief: Significant reduction in angina and other heart symptoms.
- Improved Heart Function: Enhances cardiac function by improving myocardial perfusion.
- Increased Quality of Life: Enables patients to perform daily activities more comfortably.
Risks of CTO Treatment
- Bleeding: Risk of bleeding at the catheter insertion site or procedural site.
- Perforation: Risk of arterial perforation, which can be a serious complication.
- Arrhythmias: Development of heart rhythm disturbances following the procedure.
- Contrast Agent Reaction: Allergic reactions or kidney function impairment due to contrast agents used.
Post-Treatment Follow-up and Care
After the procedure, patients should attend regular doctor visits to monitor heart function. Medications (e.g., anticoagulants, statins, beta-blockers) should be taken as prescribed, and recommended lifestyle changes (healthy diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation) should be adopted. Additionally, cardiac rehabilitation programs can accelerate recovery and improve overall health.
Conclusion
CTO treatment represents an effective and advanced option for patients with chronic total occlusions. When performed by experienced cardiologists, this method can significantly improve patients’ quality of life and alleviate symptoms. However, determining the appropriate treatment method for each patient requires comprehensive evaluation and risk analysis.
