Aortic Valve Replacement (AVR)
Aortic valve replacement (AVR) is a surgical procedure used to treat diseases of the aortic valve, such as aortic valve stenosis or aortic valve insufficiency.
Aortic Valve Replacement (AVR)
Aortic valve replacement (AVR) is a surgical procedure used to treat diseases of the aortic valve, such as aortic valve stenosis or aortic valve insufficiency. The aortic valve is located at the junction where the aorta, the main artery that carries blood from the heart, connects to the left ventricle. Aortic valve stenosis occurs when the valve leaflets become stiff and narrow, restricting blood flow. Aortic valve insufficiency, on the other hand, occurs when the valve leaflets do not close properly, causing blood to leak backward.
Procedure: AVR is typically performed as open-heart surgery and may involve the following steps:
- Anesthesia: The patient receives anesthesia to induce sleep and prevent pain during the procedure.
- Opening the Chest: A surgical incision is made on the chest and the sternum (breastbone) is opened to access the heart.
- Preparing the Heart-Lung Bypass: A heart-lung machine is used to divert blood circulation away from the heart, oxygenate it, and maintain circulation during the procedure.
- Incising the Aorta: The aorta is opened, and the heart may be temporarily stopped to perform the surgery.
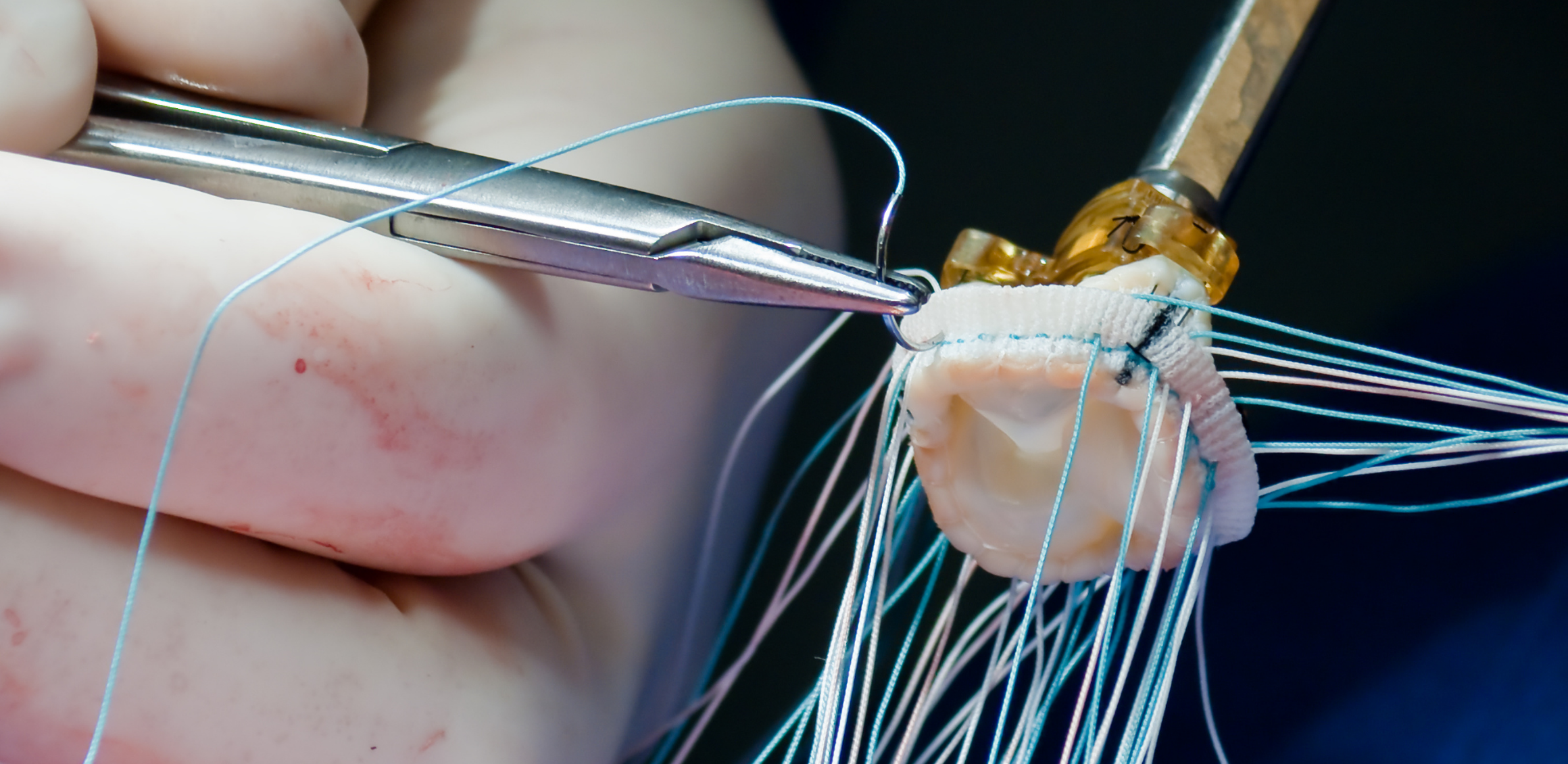
- Removing the Diseased Valve: Damaged or stiffened valve leaflets are removed from the aortic valve.
- Placing the New Valve: A prosthetic aortic valve or a biological valve is sewn into place within the aorta to replace the removed valve.
- Closing the Chest: The sternum is closed with sutures to complete the surgery.
The specific details of the AVR procedure can vary based on the severity of the aortic valve disease, the patient’s overall health condition, and other factors.
Purposes of AVR: AVR aims to alleviate symptoms of aortic valve disease, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition.
Recovery: The recovery period after AVR depends on the patient’s age, overall health, and the complexity of the surgical procedure. Hospital stay typically ranges from several days to a few weeks. It is crucial for patients to follow their doctor’s instructions and participate in a rehabilitation program to optimize recovery and regain strength after surgery.
AVR is a critical procedure that requires careful consideration of the patient’s condition and thorough planning by a specialized cardiac surgical team.
