Mitral Valve Replacement (MVR)
Mitral valve replacement (MVR) is a surgical procedure used to treat mitral valve diseases such as mitral valve stenosis or mitral valve regurgitation.
Mitral Valve Replacement (MVR)
Mitral valve replacement (MVR) is a surgical procedure used to treat mitral valve diseases such as mitral valve stenosis or mitral valve regurgitation. The mitral valve regulates the flow of blood between the left atrium (atrium) and the left ventricle (ventricle). In stenosis, the valve narrows, while in regurgitation, the valve does not close properly, causing blood to leak back.
MVR procedure is typically performed as open-heart surgery and may include the following steps:
- Anesthesia: Administering anesthesia to the patient to induce sleep.
- Chest Incision: Making an incision on the chest wall and opening the sternum (breastbone).
- Preparation of the Heart-Lung Bypass: Redirecting blood circulation through a heart-lung machine for oxygenation.
- Opening the Left Atrium: Accessing the mitral valve through the left atrium.
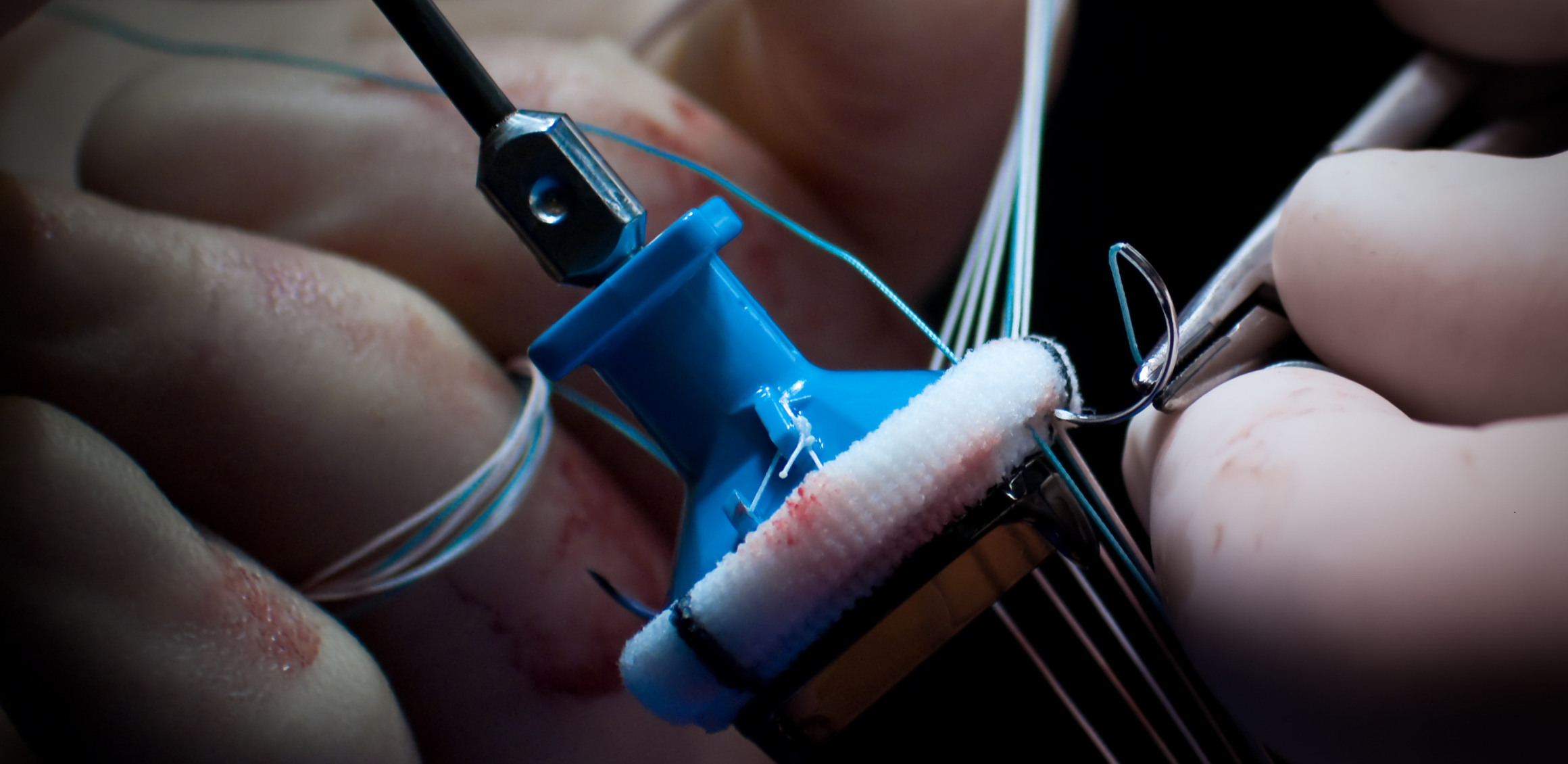
- Removal of the Old Valve Leaflets: Removing damaged or hardened mitral valve leaflets.
- Placement of the New Valve: Implanting a prosthetic or biological mitral valve into the mitral valve annulus.
- Closing the Chest: Closing the sternum and suturing the incision.
The MVR procedure can vary depending on the severity of the mitral valve disease, the patient’s overall health condition, and other factors. MVR is performed to alleviate symptoms, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of complications.
The recovery period after MVR varies depending on the patient’s age, general health condition, and the complexity of the surgical procedure. It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and rehabilitation program closely during the postoperative period.
